MeGUI is one of the newer tools that has been designed with H.264 encoding in mind, while supporting other types of conversion, such as XviD. This guide shows you how to encode a H.264 (MP4) using MeGUI from a DVD as the primary example (instructions for converting other types of video files are also included).
This guide is aimed at intermediate users, basically users that are familiar with DVD conversion/backup and want to experiment with H.264 and MeGUI. As such, basic knowledge of DVD ripping and conversion is required, although brief instructions will be provided in any case.
Software you'll need (all freeware):


 Step 1: Installation
Step 1: Installation
 Step 2: DVD Ripping
Step 2: DVD Ripping
 Step 3: D2V Creator
Step 3: D2V Creator
This step will use MeGUI's D2V Creator tool to create a D2V file needed for MeGUI/AviSynth to handle MPEG-2 files. This step is required only for MPEG-2 files - all other types of inputs do not require a D2V file and can be loaded straight into AviSynth and therefore, you can skip this step and go to the next page/step (Step 4: AviSynth Script Creator).
Start MeGUI. I like to first clear the job queues of previously finished jobs. This is optional, but it might help to make things clearer. To do this, click on the "Queue" tab and then click on the "Clear" button.
From the "Tools" menu, select "D2V Creator". In the "Video Input" section, load the first ripped VOB file of the movie titleset (the rest of the files in the set will be loaded automatically). You will get an error message about not being able to find DVD Decrypter generated info files, this is fine (as we did not use DVD Decrypter's IFO mode) and
press "OK" to skip this error.
In RipIt4Me's step 1, you were asked to take note of the audio track numbers. We'll need it here select which audio track(s) to demux - you can select more than one track if you want the encoded file to have multiple audio tracks. Alternatively, you can just select the demux all the tracks and then choose the correct audio track(s) later on.
The default save directory is the same directory as your loaded DVD VOB files - change this if you want to.
Select both the "On completion load files", "and close" checkboxes and
press the "Queue" button. You are now returned to MeGUI -
click on the "Queue" tab and press the "Start" button to start the D2V creation. When processing has finished, the status of the queued job will read "Done" and the created D2V file will be loaded into the AviSynth Script Creator ready for the next step. This can take a while, so please be patient - the status window's progress bar may not move, but don't worry, DGIndex is working
 Step 4: AviSynth Script Creator
Step 4: AviSynth Script Creator
 Step 5a: Video Encoding Options MP4
Step 5a: Video Encoding Options MP4
 Step 5b: Video Encoding Options XVID
Step 5b: Video Encoding Options XVID
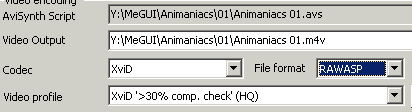
After the AviSynth Script Creator window closes, it will be entered in the AviSynth Script box on the Input tab. Below that is the output file. Click the button to the right of it to change the location or name. Select the dropdown menu next to Codec and set it to XviD. File Format should be set to AVI, MKV, or RAWASP (MP4). To select a Video Profile, determine what percentage of original DVD's bitrate will be used for the XviD encode. If you're not sure, compare the combined size of the VOB files to the intended final size of the XviD. The profiles are named by what amount of compression they're designed for. For example, XviD '>90% comp. check' means it's for encodes that are 90% as big as the original or more. Find the largest percentage that's smaller than or equal to the amount of compression your encode will have. Each compression level will have a fast and HQ option. As the names suggest, one will give you faster encodes, and the other a little higher quality.
 Step 6: Audio Encoding Options
Step 6: Audio Encoding Options
Now it's time to set up the audio encoding options. If you've followed this guide for DVD conversion, then the demuxed audio track we selected in the D2V Creator should already be loaded in (if not, load in the .ac3 file that was created). If you are not converting from a DVD source, then you can either load in a separate audio file or if you edited the AviSynth script (set "audio=true"), then load in the AVS file into the "Audio Input" section (meaning both video and audio inputs are the same AVS file). Repeat if you want a second audio track by clicking on the "2" select option.
Now we select an audio codec to use. I prefer AAC audio, especially with H.264 as video - AAC is to MP3 what H.264 is to DivX/XviD, better compression + better quality. So which audio codec should you use? I prefer ND AAC (Nero Digital), so select it if you agree with me. We can now choose an audio profile from one of the "NDAAC" options. "NDAAC-HE-64Kbps" is the one I like, as it will give you roughly the same quality as a 128 Kbps MP3 file. You can select one of the "HEPS" (HEv2) profiles if you really want a small file size. The "LC" options offer better compatibility (eg. with iPod/iTunes), but at the cost of file size (still smaller than MP3s though).
 Step 7: AutoEncode and starting the encoding
Step 7: AutoEncode and starting the encoding
 MeGUI Custom x264/AVC video profiles. (Updated: 2006-12-21)
MeGUI Custom x264/AVC video profiles. (Updated: 2006-12-21)
Instructions
Install
MeGUI and let the autoupdate run, it will automatically fetch the profiles from the autoupdate server or if you prefer get the profiles archive (below) and use the MeGUI Import Profiles option to import them.
Once imported you will find the profiles in the "Video Profiles" drop down list.
Before starting encoding set the bitrate or quantizer (manually or thru the calculator) and adjust the inloop filter accordingly to your needs/taste: keep it 1;1 or higher for anime/toons (max 3;3) and not higher than x264 defaults (0;0) for movies.
Profiles for maximizing Quality and hit a desired bitrate/filesize (2 or more passes, SLOW encoding, High Profile)
HQ-Slow: Pretty slow but not much. Quality is near the best.
HQ-Slower: Slower than HQ-Slow but it tries to squeeze some more compression thru the use of more reference frames.
HQ-Slowest: Same as HQ-Slower with more reference frames.
HQ-Insane: All settings maxed out.
Profiles for Common Encoding (2-passes)
CE-Highprofile: Common settings using high profile options (not compatible with QuickTime)
CE-Mainprofile: Common settings using main profile options (not compatible with QuickTime)
CE-QuickTime: Common settings for QuickTime 7 compatibility.
CE-Baseline: Common settings using baseline profile options (100% compatible with QuickTime 7)
Profiles for maximizing Speed and hit a desired bitrate/filesize (1-pass)
1P-Maxspeed: Everything disabled for max encoding speed (good for live capturing).
1P-Intermediate: Intermediate settings for average speed and final quality.
1P-Goodquality: Settings for good quality with 1 pass.
Profiles for constant Quality/Quantizer (1-pass)
CQ-Lossless: Lossless encoding.
CQ-ASP_Q2_equiv: Almost the equivalent of MPEG-4 ASP Q2 encoding.
CQ-ASP_Q2_eq(crf): Same as above but with "constant quality" (constant rate factor).
Profiles for Anime/Toons (2 passes)
AE-Standard: 2 passes, Main Profile, standard quality.
AE-Goodquality: Slower than AE-Standard, High Profile, higher quality.
AE-Maxquality: Slowest mode with maxed out settings, best quality.
Profiles for Consoles and Portable Devices
PD-PSP: Profile for Sony PSP playback.
PD-Xbox_Hires: Profile for MS XBOX and higher than 512pixels resolution (latest XBMC is needed).
PD-Xbox_LoRes: Profile for MS XBOX and lower than 512pixels resolutions (latest XBMC is needed).
PD-iPod: Profile for iPod Video based on
Arstechnica settings.
PD-iPod 5.5G: Profile for the new iPod 5.5G.
Profiles for HD-DVDs
SA-HD-DVD: First EXPERIMENTAL Profile for HD-DVD.
Url to this pages:
http://nade.dk/web/nade/site.nsf/FramesetHP?readform&wmain=files/Megui